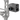When the lights go out, your eyes are no longer much help — but a thermal imaging device can still see clearly. How? By detecting heat instead of visible light.
In this article, we’ll break down how thermal imaging works, where it’s used, and why it’s becoming an essential tool for professionals and civilians alike.
🔥 What Is Thermal Imaging?
Thermal imaging (also called infrared thermography) is the process of capturing the heat energy emitted by objects and converting it into a visible image. Unlike regular cameras that depend on reflected light, thermal cameras see the world based on temperature differences.
Everything above absolute zero (-273.15°C or -459.67°F) emits infrared radiation. The hotter an object is, the more infrared energy it gives off.
A thermal imaging camera collects this radiation and turns it into an image where different temperatures are displayed in colors or shades — typically:
White/yellow/red = warmer objects
Blue/black/purple = cooler objects
🧠 How Does a Thermal Imaging Device Work?
At the core of every thermal imager is an infrared sensor that detects tiny variations in temperature. Here’s how the process works step by step:
Infrared Detection:
The lens captures infrared radiation (heat) from all objects in its field of view.
Sensor Processing:
The sensor array (often made of vanadium oxide or amorphous silicon) converts this heat into electrical signals.
Image Processing:
A built-in processor translates the electrical signals into a thermal image. The device then displays this image on a screen, with different colors or shades representing different temperatures.
User Interpretation:
The user can spot heat signatures — like humans, animals, machinery, fire, or even hot electrical components — regardless of lighting conditions.
Unlike night vision, thermal imaging does not need any light at all to function — it can even see through smoke, fog, and complete darkness.
🛠️ Common Uses of Thermal Imaging
Thermal imaging is used in a wide range of industries:
Firefighting: Locating people through smoke, detecting hotspots
Search and Rescue: Finding missing persons in remote areas
Security & Surveillance: Detecting intruders at night
Building Inspection: Identifying heat leaks, water damage, or insulation issues
Automotive: Assisting with nighttime driving or detecting overheated components
Outdoor & Wildlife: Spotting animals in low-visibility environments
🧊 Cool Tech — With Hot Results
One of the biggest advantages of thermal cameras is that they work where the human eye (and even night vision) cannot. Whether you're navigating a smoky hallway or scanning a dark forest, thermal imaging reveals what would otherwise stay hidden.
🎯 Why GTGUARD’s AI15 Thermal Imager Stands Out
At GTGUARD, we developed the AI15 Thermal Imaging Device with professionals in mind — but made it compact and affordable enough for outdoor enthusiasts and security personnel too.
High sensitivity thermal sensor
Full-screen thermal display
Long detection range
Easy-to-use interface
Optional recording and Wi-Fi sharing
Whether you're a firefighter, a search & rescue volunteer, or just someone who loves to explore after dark — the AI15 gives you the power to “see the unseen.”
📢 Stay Tuned – More Innovation Ahead
We're constantly improving our thermal imaging technology and will soon launch new models with higher resolution, faster refresh rates, and even color enhancement modes.
Learn more: https://gtguardhunt.com/products/hawkeye-ai15-thermal-monocular
👉 Subscribe to our newsletter or follow us on Facebook to get early access, discounts, and news about upcoming giveaways!